india natural vegetation » What Is A Natural Vegetation
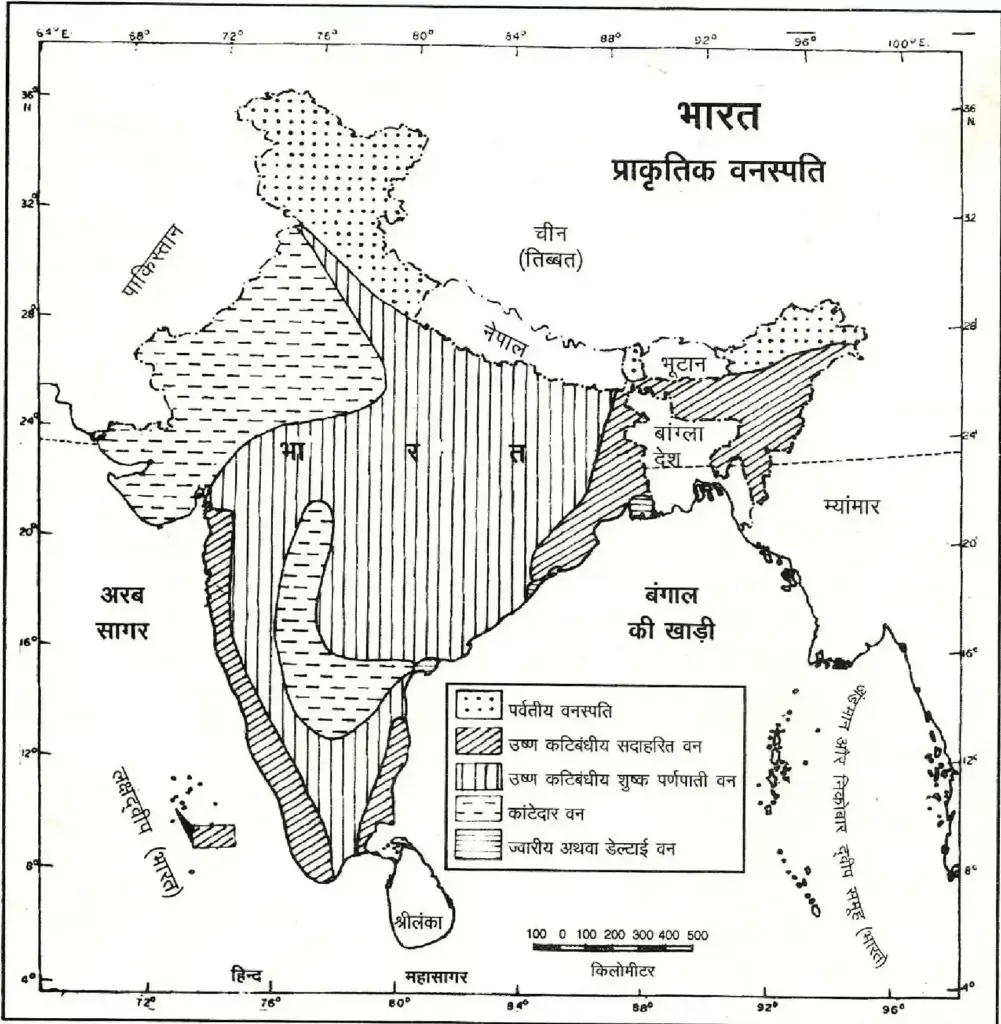
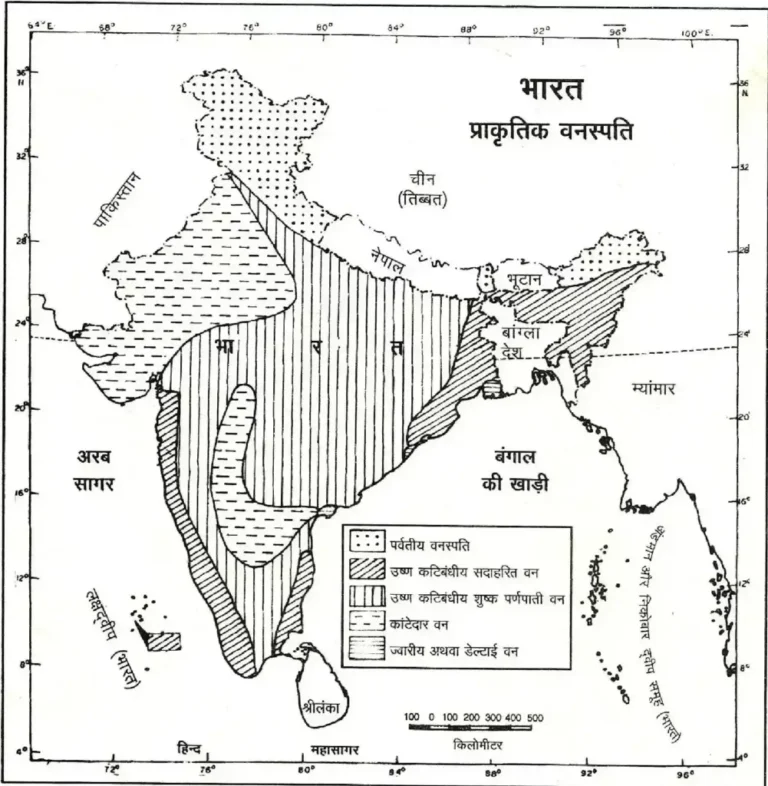
types of natural vegetation of india
| Plant Site | Rain | Area | Characteristics Of Plants | Tree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tropical Moist Evergreen Forest | The Annual Rainfall Is 250 Cm. Area With High Temperature And Humidity Throughout The Year | 900 M In The Tree Area Below. Western Ghats, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, Small Parts Of West Bengal, Coastal Orissa, Andaman-Nicobar And North-Eastern Region. | They Never Drop Their Cards All At Once And Are Arranged In Tiers Three And Four. | Mainly Hardwood Trees- Rajwood, Mahogany, Ebony, Ebony, Bamboo, Rubber, Cinchona, Sandal Etc. |
| Tropical Semi-Evergreen Forest | 200 To 250 Cm Annual Rainfall | It Forms A Narrow Strip Of Evergreen Forest On The Eastern Side Of Assam, West Bengal, Coastal Orissa, And The Western Ghats. | The Tree Canopy Is Less Dense And Consists Of Stems And Epiphytes. , , There Is Prominence. Vegetation Is The Transition Between An Evergreen Tree And A Deciduous Tree. | Main Trees – Kadam Rosewood, Kanju, Champa And Mango |
| Tropical Deciduous Forest | Rain 200 Cm. Less Than 156–200 Cm. Rainy Monsoon Forest <156 Cm. Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests Containing Rain . | West Bengal, Orissa Chotanagpur Plateau, Eastern Slope Of Western Ghats And Lower Himalayas | Trees Shed Their Leaves For Six To Eight Weeks In Summer To Reduce Tree Transpiration. | Sal In The North, Teak In The Central And Western Part, Sandalwood In The South-North Part. Siso, Mahua, Neem Khair Etc. |
| Tropical Thorny Forest | 50-75 Cm. Rain | Interior Plateau, Eastern Rajasthan, Eastern And Northern Punjab, Northern Gujarat, Parts Of Andhra Pradesh. | Small Thorny Trees That Fall Up To 10 M. The Coasts Are High. | Acacia, Acacia, Euphorbia, Khair, Date Etc. |
| Desert Vegetation | Annual Rainfall From 10-50 | Western Part Of Rajasthan. | The Bushes Are Spread Far And Wide. | Cactus, Thorny Shrubs Etc. |
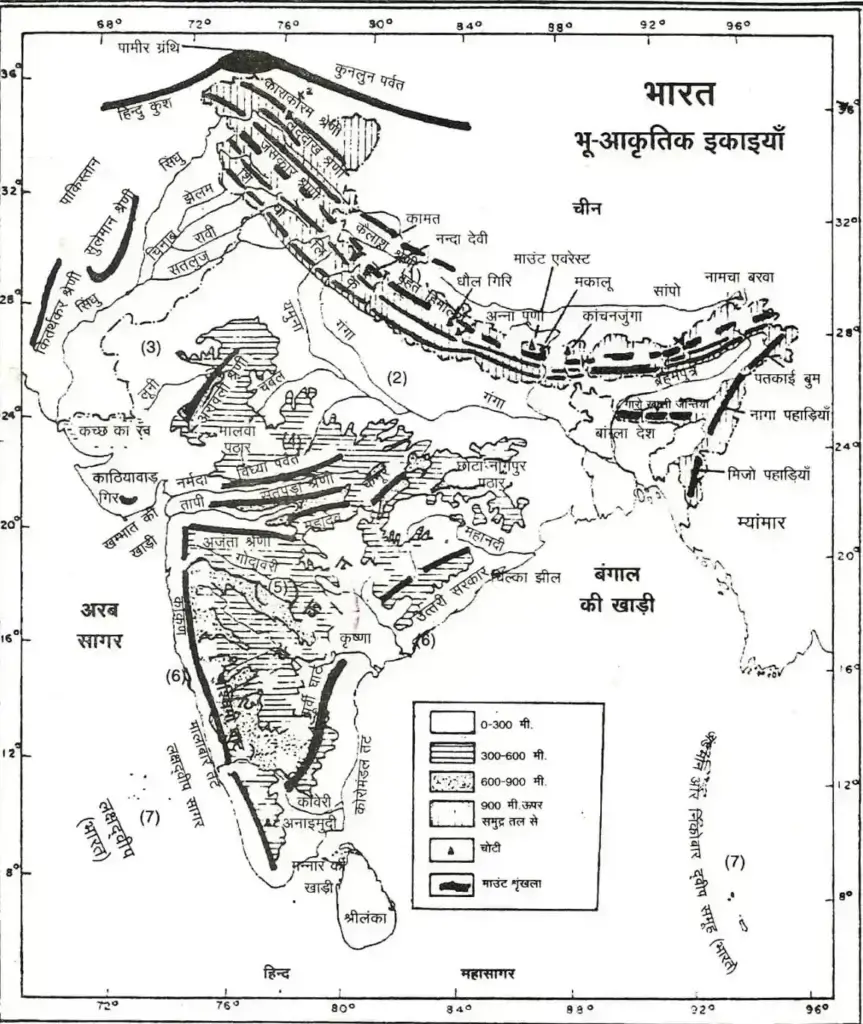
| Himalayan Flora | Rain 75 Cm. 125 Cm From In Between | Hilly Regions Of The Himalayas, Jammu And Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh. | Vegetation Changes With Altitude | Trees With Broad Leaves And Angular Shape Are The Main Vegetation. Such As Pine, Oak, Pine, Deodar, Blue Pine, Silver Fir Etc. (In The Western Himalayas) And Oak, Laurel And Chestnut (In The Eastern Himalayan Region). |
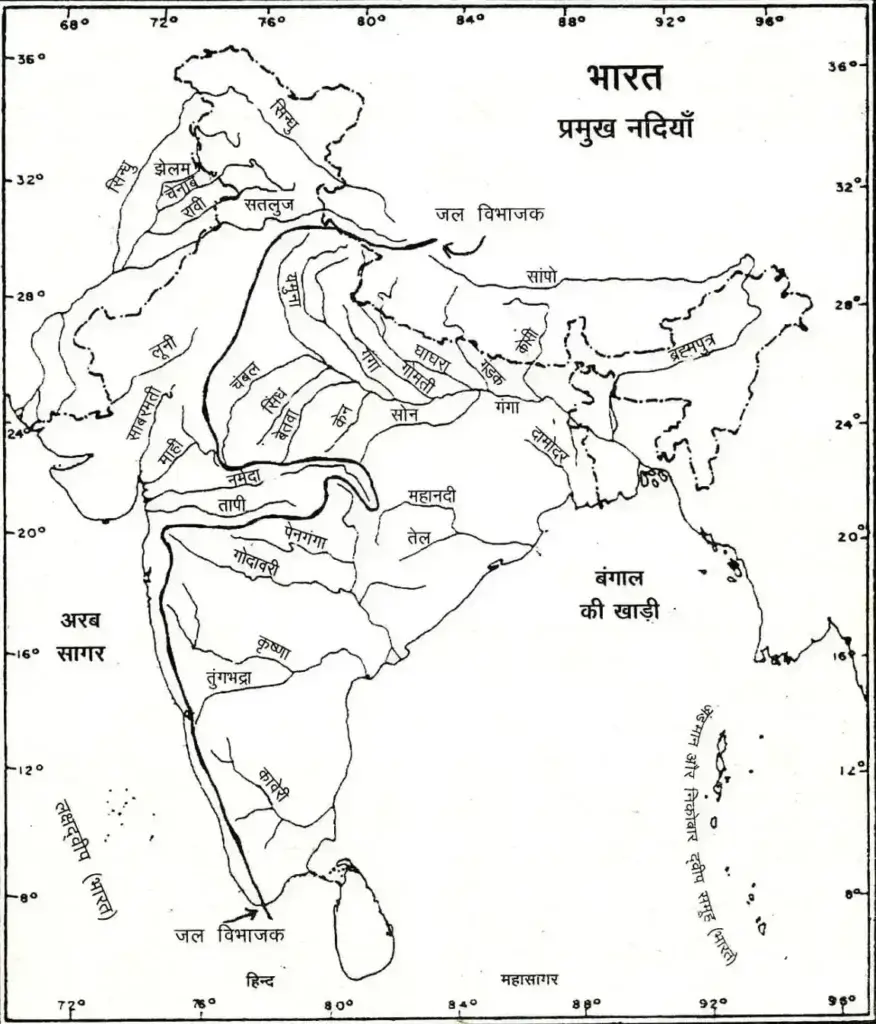
| Mangrove Vegetation | On Average 40 To 200 Cm. Rainfed Areas | Very Dense At Some Places – Western Ghats, Ganga, Mahanadi, Krishna, Kaveri And Godavari Deltas. Sandarvan Above Example. | Due To The Tide, The Salt Water Mixes With The Clean Water In The Lower Coastal Area, Such Vegetation Is The Most. Which Help In The Production Of Stilt Roots And Which Have Innumerable Ascending Vines. | Sundari, Coconut, Pine, Kewra, Cane, Crew Etc. |
| Subtropical Wet Mountain Forest | Rainfall 150-300 Cm. Between Me | 900 M In The Eastern Himalayas. Above And In The Western Himalayas. | Mixed Forest Of Angular Tree And Earth Tree | Pine And Oak |
| Temperate Forest | 1830 M. Higher Than The Eastern | In The Himalayas And 1500 M. In The Western Himalaya Region At Higher Altitudes. | Evergreen Coniferous Forest | Cedar, Indian Chestnut, Magnolia, Blue Pine, Oink And Hemlock. | |
| Alpine Forest | 3650 M In The Eastern Himalayas. To The Height | The Plants Are So Small And So Close Together That They Form A Layer Of Soft Carpet. | Sus, Fur, Verch, | Juniper And Rhododendron Are Found In Rocky Areas On Top Of Alpine Vegetation And Grassy Vegetation, Where Some Moss And Some Herbs Are Found Until A Permanent Snow Line Is Reached. |
Note: – According To The National Forest Policy , 33.3% Of The Country’s Area Should Be Covered By Forests.
Forest Related Facts
According To The 12th Forest Status Report-2011, The Total Forest Area Is 692027 Sq.Km. Is. (21.05% Of The Total Land Area)
States With Highest Forest Area In The Country
- 1. Madhya Pradesh
- 2. Arunachal Pradesh
- 3. Chhattisgarh
- 4. Maharashtra
States With Minimum Forest Area In The Country
- 1. Haryana
- 2. Punjab
- 3. Goa
- 4. Sikkim
States/Union Territories With Highest Percentage Of Geographical Area (Relative To Their Geographical Area)
- 1. Mizoram (90.28%)
- 2. Lakshadweep (84.38%)
- 3. NVS (81.51%)
- 4. Arunachal Pradesh (80.50%)
States/Union Territories With Largest Mangrove Area
- 1. W. Bengal (2152 Sq Km)
- 2. Gujarat (1064 Sq. Km.)
- 3. NDDS (615 Sq. Km.)
States With Highest Number Of Bamboo Forests In The Country
- 1. Arunachal Pradesh
- 2. Madhya Pradesh
- 3. Maharashtra
what is a natural vegetation
The Country’s Area Should Be Covered By Forests.
What is The National Forest Policy
According To The National Forest Policy , 33.3% Of The Country’s Area Should Be Covered By Forests.
india natural vegetation
According To The 12th Forest Status Report-2011, The Total Forest Area Is 692027 Sq.Km. Is. (21.05% Of The Total Land Area)