Respiratory System of a Human
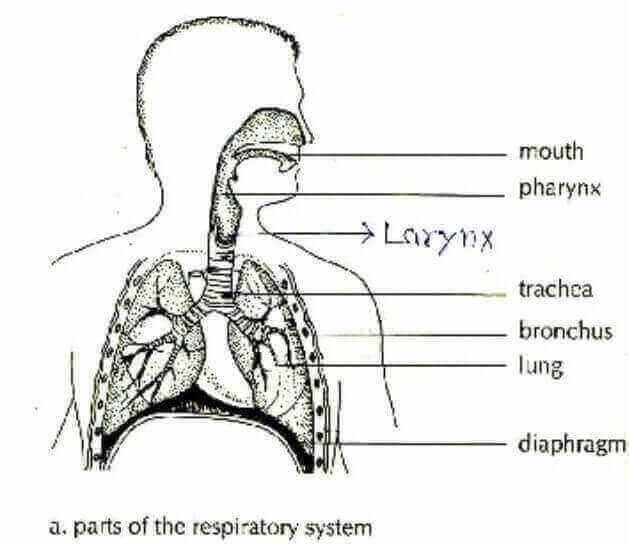
Respiratory System Is Called ‘ Respiratory System ‘, The System That Exhales And Exhales Air In The Form Of Breathing Inside The Body .
Under This Name, Larynx , Epiglottis , Windpipe , Bronchus And Lungs Come.
These Systems Mainly Act As Airways Inside The Body.
In These- ‘ Epiglotis ‘ Closes The Respiratory Tract While Swallowing Food.
The Windpipe Is Made Of Cartilage ( Flexible Bone ) .
The Purification Of Blood In The Lungs Takes Place Through The Exchange Of Gases.
The Exchange Of Gases Takes Place Through The Air Alveoli .
Oxygen Enters The Blood From The Alveoli And Carbon Dioxide From The Blood Enters The Alveoli.
There Are 300 To 400 Million Air Alveoli In The Lungs Of An Adult Human.
In Humans, The Right Lung Is Divided Into Three Bodies And The Left Lung Into Two Bodies.
The Gaseous Exchange In The Alveoli Occurs Through Diffusion.
Emphycema Disease Is Related To The Lungs .
This Disease Is Caused By Excessive Cigarette Smoking, In Which The Alveoli Of The Lungs Are Damaged And The Action Of Gaseous Exchange Is Affected.
A Covering Of A Membrane Called Pleura Is Found Over Them To Protect The Lungs .
Respiration
Respiration The Energy Produced By The Oxidation Of Glucose. Is Called.
Respiration Is A 24-Hour Process In Living Organisms.
Type Of Respiration
There Are Two Types Of Respiration Which Are Called Oxy And Anoxic Respiration Respectively.
Aerobic Respiration _ _
- The Complete Breakdown Of Glucose In The Presence Of Oxygen Is Called Aerobic Respiration .
- In The Process Of Oxygen Respiration, Energy Is Produced In The Form Of 38 ATP.
- The Process Of Oxygen Respiration Takes Place Inside The Cytoplasm And Mitochondria Of The Cell.
- Glucose Is Broken Down Into Pyrvic Acid By The Process Of Glycolysis In The Cytoplasm.
- During This Fission, Energy Is Produced In The Form Of 2 ATP.
- Glycolysis Is Considered To Be The Common Step Of Oxygen And Anoxic Respiration.
- The Action Of The Krebs Cycle Takes Place Inside The Mitochondria.
- Pyrvic Acid Breaks Down Into Carbon Dioxide And Water During The Krebs Cycle.
- During This Fission, Energy Is Produced In The Form Of 36 ATP.
- Pyrvic Acid Dissociates Both In The Presence And Absence Of Oxygen.
- When Humans Do More Work, In The Absence Of Oxygen In The Muscles, Pyrvic Acid Breaks Down Into Lactic Acid And Carbon Dioxide.
- The Accumulation Of Lactic Acid Causes Muscle Pain.
Anaerobic Respiration
The Oxidation Or Release Of Glucose In The Absence Of Oxygen Is Called Anaerobic Respiration .
The Cause Of Muscle Pain Is Also Believed To Be The Lack Of Energy In The Respective Cells Because In The Process Of Anoxic Respiration, Energy Is Produced In The Form Of 2 ATP.
When Anoxic Respiration Occurs In Bacteria And Fungi, It Is Called Fermentation .
Alcohol And Vinegar Are Produced By The Process Of Kindavan.
Breathing
Generally The Act Of Breathing Is Called Exhalation.
Energy Is Not Produced In This Process.
The Process Of Taking Atmospheric Oxygen Into The Lungs And Releasing Carbon Dioxide Gas From Different Parts Of The Body Into The Atmosphere Is Called Respiration.
Respiration Begins With The Activation Of The ‘ Diaphragm ‘ .
During Respiration, The Largest Amount Of Nitrogen Gas (78%) Is Taken In And The Maximum Amount Of Nitrogen (78%) Is Released.
Oxygen 21% Is Taken In And 16% Is Given Out.
Carbon Dioxide .03% (In The Same Amount In The Atmosphere) Is Absorbed And 4% Is Released.
On Taking A Deep Breath, 3- Liters Of Gas Is Consumed, This Capacity Is Called ‘ Vital Capacity ‘ .
In Normal Breath – Liters Of Gas Is Taken, Which Is Called ‘ Tidal Capacity ‘ .
– Liter Of Gas Remains In The Lungs In Every Condition
Which Is Called ‘ Residual Capacity ‘ . The Maximum Gas-Holding Capacity Of The Lungs Is 5 Liters.
The Uptake Of Oxygen And The Release Of Carbon Dioxide Depend On The Amount Of Hemoglobin .
The Exchange Of Gases Takes Place By The Process Of Diffusion.
Cellular Respiration Takes Place Inside Cells Through Two Cycles – Glycolysis And Crevice, And The Formation Of Carbon Dioxide And Water.
Anoxyrespiration Occurs In The Absence Of Oxygen.
In This, The Decomposition Of Carbohydrates Results In The Formation Of Ethyl Alcohol And Water.
Over-Exertion Leads To The Build-Up Of “Lactic Acid”, Which Makes One Feel Tired.
Carbon Dioxide Is Transported Mainly In The Form Of Bicarbonate Ion (HCO3).
Blood Can Exchange 2% Of Oxygen Even In The Absence Of Haemoglobin.