What is topography | topography meaning | World topography

Topography meaning – Earth’s Surface Is Extremely Heterogeneous And These Asymmetries Have Also Been Formed By Different Processes. These Asymmetries Found On The Surface Of The Earth Are Called Topography. These Are Divided Into The Following Categories:
1. Class I : Continental And Oceanic Basin 2
, Secondary Range: Mountains, Plateaus, Plains Etc.
3. Third Class: Lake, River, Valley, Gorge, Waterfall, Mooren, Sand-Stupa.
Continents And Oceans
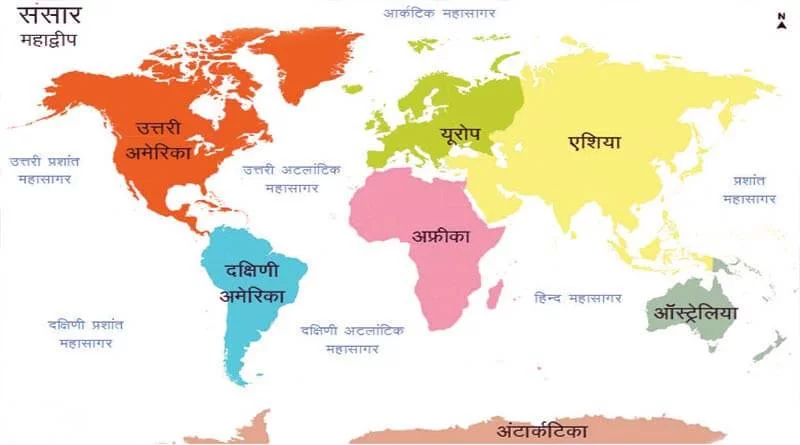
There Are Seven Continents And Four Major Oceans On Earth.
Topography Continent
The Vast Land On The Surface Of The Earth Is Called A Continent. Most Of The Arid Regions Of The Earth Are Found On The Continents. There Are A Total Of Seven Continents On Earth, Which Are In Descending Order Of Area: 1. Asia 2. Africa 3. North America 4. South America 5. Antarctica 6. Europe 7. Australia
Topography ocean
The Vast Water Body Found On The Surface Of The Earth Is Called Ocean. All The Aquatic Parts Are Interconnected, However They Are Divided Into Five Main Parts Which Are In Decreasing Order Of Size As Follows:
1. Pacific Ocean 3. Indian Ocean 2. Atlantic Ocean 4. Arctic Ocean.
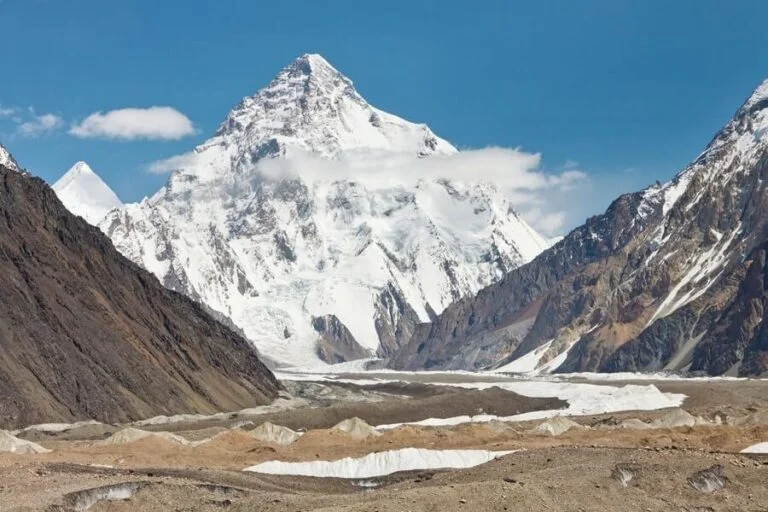
Topography mountains
The Mountain Is Called The Second Order Relief. It Is Such An Elevated Part Of The Earth’s Surface Whose Slope Is Sharp And The Peak Area Is Narrow. These Are Generally Elevated Areas Above 600 M. Some Mountains Are More Than 8000 Meters High. In Some Mountains There Is A River Of Permanently Frozen Ice Which Is Called Glacier. There Are Some Mountains Which Are Not Visible Because They Are Within The Sea.
The Study Of Mountains Is Called Orology .
Types Of Mountains
1. Fold Mountains: When Folds Are Formed In The Rocks By The Force Of Compression, It Is Called Folded Mountains. The Largest Extension Of Fold Mountains Is Found In The World. Examples Of Folded Mountains Are Himalaya, Alps, Rocky, Andes, Ural Etc.
Note: The Aravalli Range Of India Is One Of The Oldest Fold Mountains In The World.
2. Block Mountain: This Mountain Is Formed By The Tensional Force. Due To The Tensional Force, Some Part Of The Crust Gets Raised And Some Part Gets Pushed Down. The Elevated Part Is Called Block Mountain And The Submerged Part Is Called Rift Valley. Examples Are Vosges (France), Black Forest (Germany), Sierra Nevada, Salt Range Etc.
3. Volcanic Mountains: These Are Also Called Mountains Of Accumulation. They Are Formed By The Deposition Of Ejected Material As A Result Of Volcanic Eruption. For Example, Mount Kilimanjaro (Africa), Fujiyama (Japan) Etc. 4. Residual Mountains : They Are Formed By Erosion And Friction Of Early Mountains (Fold, Block Or Volcano). Aravalli Mountain Is An Example Of Residual Mountain. Apart From This, Examples Are Nilgiri, Parshvanath, Girnar, Rajmahal, Sierra (Spain) And Coskill (New York).
| Chain | Location |
|---|---|
| Andes | South America |
| Himalaya-Karakoram-Hindu Kush | South Central Asia |
| Rocky | North America |
| Great Dividing Range | Eastern Australia |
| Western Ghats | Western India |
| Caucasus | Europe, Asia |
| Alaska | America |
| Alps | Europe |
| Apenain | Europe |
| Ural | Asia |
Topography Plateaus
- The Plateau Is A Second Grade Relief. It Covers One Third Of The Crust. The High Land Raised At Least 300 Meters Above Sea Level, Whose Summit Is Flat And Flat, Is Called Plateau. The Slopes Along The Edge Of The Plateau Are Steep.
- Like Mountains, Plateaus Can Also Be New Or Old. The Deccan Plateau Of India Is One Of The Oldest Plateau. The East African Plateau (Kenya, Tanzania And Uganda) And The Western Plateau Of Australia Are Other Examples.
- Tibet Is The Highest Plateau In The World With An Altitude Of 4000-6000 Meters Above Sea Level.
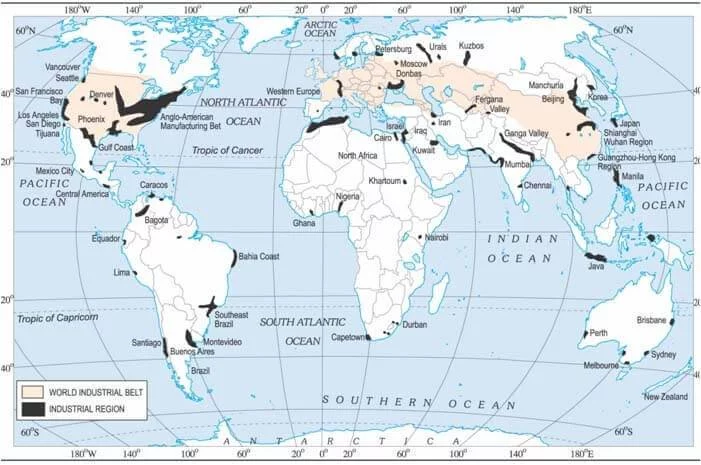
- Plateaus Are Quite Useful As They Are The Deposits Of Minerals. This Is The Reason That Most Of The Mining Areas In The World Are Located In The Plateau Region. The African Plateau Is Famous For Gold And Diamond Mines. Large Deposits Of Iron, Coal And Manganese Are Found In The Chotanagpur Plateau In India.
| Desert | Area (Km) | Extension Area |
|---|---|---|
| Help | 84,00,000 | Algeria, Chad, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, Egypt And Morocco |
| Australian | 15,50,000 | Great Sandry, Great Victoria, Simpson, Gibson And Stuart Desert Areas |
| Arabian | 13,00,000 | Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Syria, And Nafud Region |
| Gobi | 10,40,000 | Mongolia And China |
| Kalahari | 5,20,000 | Botswana (Central Africa) |
| Takla Maken | 3,20,000 | Siqiang (China) |
| Sonoran | 3,10,000 | Arizona And California (USA And Mexico) |
| Namib | 3,10,000 | Southern Africa (Namibia) |
| Karakum | 2,70,000 | Turkmenistan |
| Thar | 2,60,000 | North-Western India And Pakistan |
An Island Is Such A Part Of An Island Landmass That Is Surrounded On All Sides By Aquatic Parts. On The Basis Of Origin The Islands Can Be Divided Into Five Parts:
Tectonic Islands: Such Islands Are Formed Due To Land Subsidence, Uplift, Formation Of Rift Basins Or Separation Of Continental Landmass Through Geologic Activities. This Process Has Led To The Formation Of More Islands In The Atlantic And Pacific Ocean.
Depositional Islands: These Islands Are Formed By The Deposition Of Sediments By Various Factors (Eg Rivers, Glaciers, Ocean Currents).
Erosional Island When The Soft Rocks Are Eroded And The Hard Rocks Remain In Place, Then The Water Accumulation Around It Forms The Island, Which Is Called Erosional Island. The Island Of Greenland Was Formed By Glacial Erosion.
Volcanic Islands When Lava Deposits Eject From The Sea Surface, They Form Islands. Examples Are The Hawaiian Islands, The Aleutian Islands, Etc.
Coral Islands An Island Formed From The Skeletons Of Coral Insects Is Called An Atoll. Examples Of This Are Lakshadweep, Maldives, Bermuda, Etc.Show 102550100 EntriesSearch:
| Island | Location | Area (Sq.Km) |
|---|---|---|
| Greenland | Arctic Ocean | 21,75,000 |
| New Guana Ocean | Western Pacific | 789,900 |
| Bornia | Indian Ocean (Largest In The Indian Ocean) | (751,000) |
| Madagascar | Indian Ocean | (587,041) |
| Baffin Island, Canada | Arctic Ocean | (5,07,451) |
| Sumatra, Indonesia | Indian Ocean | (4,22,200) |
| Honshu, Japan | North Pacific | (2,30,092) |
| Great Britain | North Atlantic | (2,29,849) |
| Victoria Island, Canada | Arctic Ocean | (2,17,290) |
| Ellesmere Island, Canada | Arctic Ocean | (1,96,236) |
Straits
A Strait Connects Two Different Water Bodies And Separates Two Landmasses. It Has Its Own Distinct Commercial And Strategic Importance.Show 102550100 EntriesSearch:
| Strait | Connects | Event |
|---|---|---|
| Strait Of Malacca | Andaman Sea And South China Sea | Indonesia-Malaysia |
| Palk Strait | Palk Bay And Bay Of Bengal | India-Sri Lanka |
| Sunda Strait | Java Sea And Indian Ocean | Indonesia |
| Yucatan Strait | Gulf Of Mexico And Caribbean Sea | Mexico-Cuba |
| Messina Strait | Mediterranean | Italy-Sicily |
| Orto Strait | Adriatic Sea And Ionian Sea | Italy Albania |
| Bab-El-Mandeb Strait | Red Sea-Gulf Of Aden | Yemen Djibouti |
| Cook Strait | South Pacific Ocean | New Zealand |
| Mozambique Channel | Indian Ocean | Mozambique Malagasy |
| North Channel | Irish Sea And Atlantic Ocean | Ireland-England |
Lakes
- The Water Body Which Is Stored In A Trough On The Surface Of The Earth And Is Covered By Landmass On All Sides Is Called A Lake.
- Tectonic Lakes: Lake Titicaca, Caspian Sea
- Rift Valley Lakes: Tanganyika, Malawi, Rudolph, Edward, Albert, Dead Sea.
- Lakes Associated With Volcanic Action (Crater Lake, Caldera Lake): Lake Oregon, Lake Toba.
- The Lake Formed By The Deposition By The River : Gokhur Lake |
- Lakes Formed From Marine Deposits: Lagoons, Deltas.
- Cart Lake: Lake Scotari In Yugoslavia
- Circ Or Tarn Lake: Red Tarn Lake (UK)
- Kettle Lake: Ocrane (Scotland)
| Name | Country |
|---|---|
| Caspian Sea | Kazakhstan, Russia, Turkmenistan |
| Superior | America-Canada |
| Victoria | Uganda-Kenya-Tanzania |
| Aral Sea | Kazakhstan-Azerbaijan |
| Huron | America-Canada |
| Michigan | America |
| Tangaika | Burundi-Tanzania-Zambia-Zaire |
| Baikal | Russia |
| Great Beer | Canada |
| Trust | Tanzania-Mozambique-Malawi |
| (A) Largest Fresh Water Lake (By Volume Of Water) | Baikal (Siberia) |
|---|---|
| (B) The Largest Fresh Water Lake | Superior |
| (C) Highest Navigable Lake | Titicaca (Bolivia) |
| (D) Deepest Lake | Baikal (Siberia) |
| (E) Largest Salt Water Lake | Don Juan |
| (1) Lowest Lake (2500 Feet Below Sea Level) | Dead Sea |
| (G) Meteoric Crater Lake | Lonar (In Maharashtra, India) |