What Is a Tissue | Definition Of Tissue | Tissue type
What Is a Tissue – That Group Of Cells, Which Have The Same Origin, Structure And Function, Is Called ‘Tissue’ . Tissues Are Studied In Histology Or Histology. They Are Of Different Types In Animals And Plants.
Animal Tissue
There Are 5 Types
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue : These Are Mainly Found On The Outer And Inner Surface Of The Organs. These Are Also Found In Some ‘Secretary Glands’ Such As Mammalary Glands, Sweat Glands Etc. ,
Muscular Tissue
Muscular Tissue : These Are Mainly Called The Construction Of Muscular Parts And Walls Of Hollow Organs. These Are Found In The Inner Part Of The Organs. For Example, Heart Tissue, Liver Tissue, Kidney Tissue Etc.
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue : These Work To Connect 2 Or More Tissues. For Example, Blood Tissue, Ligament, Cartilage, Etc.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous Tissue : The Unit Of Nervous Tissue Is Called Neuron . The Main Function Of The Nervous Tissue Is To Receive The Sensations And Transmit Them To The Brain And The Order Given By The Brain To The Desired Organ, Which It Does Through ‘Neurons’. Sensations Are Conducted In The Form Of ‘Chemico Magnetic Wave’. The Name Of This Chemical (Chemical Substance) Is Acetylcholine = 1
Reproductive Tissue
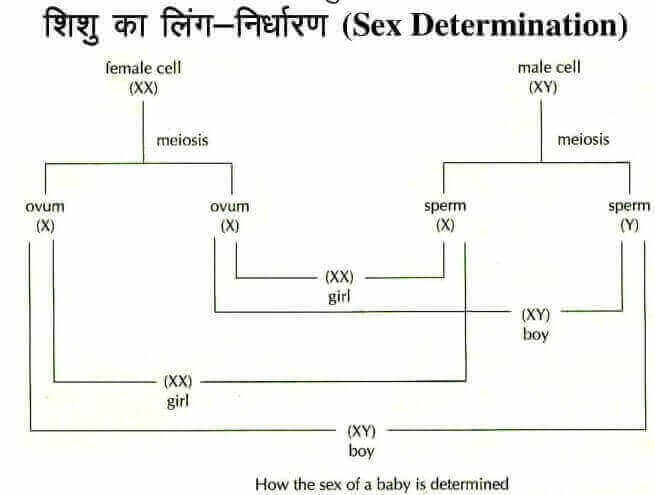
These Are Found In The Germ Cells Which Produce ‘Sperm’ In The Male And ‘ Ova ‘ ( Ova ) In The Female .
The Tissues Found In The Body Of Animals Are Divided Into The Following Categories – Epithelial Tissue, Connective Tissue, Muscle Tissue And Nervous Tissue.
Epithelial Tissue Is Found On The Outer, Inner Or Free Surfaces Of Animals.
Epithelial Tissue Lacks Blood Cells And Their Cells Are Nourished By Lymph Through Diffusion.
Epithelial Tissue Is Found On The Outer Surface Of The Skin, Around The Heart, Lung And Kidney And On The Wall Of The Genital Glands.
Epithelial Tissue Provides Protection To The Internal Parts Of The Body. The Tissue That Connects All The Organs And Other Tissues Of The Body Together Is Called Connective Tissue.
The Main Function Of Connective Tissues Is To Regulate The Temperature Of The Body And To Supply New Cells To The Tissues By Destroying Dead Cells.
Fluid Tissue Like Blood And Lymph Is Helpful In Vascularity.
The Tissue That Produces All The ‘ Muscles ‘ Of The Body Is Called Muscle Tissue .
Muscular Tissue Is Divided Into Three Types Like Unstriped, Striped And Cardiac Non – Straight Tissues Are Found In Involuntary Moving Organs Alimentary Canal, Rectum, Bladder, Blood Vessels Etc.
Non-Straight Muscles Control The Movements Of All Those Organs Which Move Themselves.
Lined Muscles Are Found In Those Parts Of The Body. That. Move At Will.
Often One Or The Other Of These Muscles. Both Ends Are Modified And Attached To The Bones In The Form Of Tendons.
Cardiac Muscle Is Found Only In The Walls Of The Heart. Heart Rate Is Due To These Muscles.
A Total Of 639 Muscles Are Found In The Human Body.
The Gluteus Maximus (Hip Muscle) Is The Largest And The Stapidius Is The Smallest Muscle In The Human Body. The Nervous System In Animals Is Formed By The Nervous Tissue .
Nerve Tissue Is Made Up Of Two Specific Types Of Cells Namely Neurons And Neuroglia.
Nervous Tissue Controls All Kinds Of Involuntary And Voluntary Actions In The Body.
Plant Tissue
These Are Of 2 Types
Meristmatic Tissue
( I ) Meristmatic Tissue
It Is The Fastest Dividing Tissue. These Are Found In The Top Part Of The Plants (Increased Work-Height), Lateral Part (Increased Work-Stem Thickness), Inter-Calary Part (Formation Of Work Branches).
These Tissues Also Perform The Function Of Food Production In The Presence Of Chloroplasts. They Also Act As Food Storage (In The Parenchyma Tissue Parenchyma Tissue).
Permanent Tissue
(Ii) Permanent Tissue
When The Dividing Capacity Of The Growing Tissue Is Exhausted, They Form Permanent Tissue.
Its Main Functions Are Food Production, Food Storage And Internal Support (Strengthening The Cell).
Complex Tissue: When More Than One Permanent Tissue Joins, ‘Complex Tissue’ Is Formed. These Are Of 2 Types.
(I) ‘ Xylem ‘
(Ii) ‘ Phloem ‘
The Main Function Of ‘Xylem’ Is To Absorb Water And Mineral Salts From The Ground And Reach The Entire Part Of The Plant. The Function Of ‘Phloem’ Is To Transport The Food Made By The Leaves To The Root Of The Plant. The ‘Xylem’ Acts Against The Gravitational Force And The ‘Phloem’ Acts Towards The Gravitational Force.
- Ligament (Muscle Tissue) This Connects One Bone To Another.
- Tendon (Tendon Tissue) Connects Muscles To Bones.
- What Is The Unit Of ‘Nervous Tissue’?
- -‘Neuron’
- Through Whom Does The ‘Nerve Tissue’ Transmit The Sensations To The Brain?
- -‘Neurons’ |
- Who Does The Work Of Transporting The Food Made By The Leaves To The Root?
- – Phloem.
- How Do Senses Conduct In Nerve Tissue?
- -Chemico Magnetic Wave.
- Which Tissue Does The Work Of Absorbing Water And Mineral Salts From The Ground And Transporting Them To All Parts Of Plants?
- -Xylem
What Is Tissue
That Group Of Cells, Which Have The Same Origin, Structure And Function, Is Called ‘Tissue’ . Tissues Are Studied In Histology Or Histology. They Are Of Different Types In Animals And Plants.
Tissue type
( I) Epithelial Tissue
( Ii) Muscular Tissue
( Iii) Connective Tissue
( Iv) Nervous Tissue
( V) Reproductive Tissue
Plant Tissue
( I ) Meristmatic Tissue
(Ii) Permanent Tissue
Definition Of Tissue
That Group Of Cells, Which Have The Same Origin, Structure And Function, Is Called ‘Tissue’ . Tissues Are Studied In Histology Or Histology. They Are Of Different Types In Animals And Plants.