What Is Earth » Age, Radius, Earth Plates, Rotation, Warming
What is Earth » Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system and the only known celestial body to support life. It is the fifth-largest planet by diameter and the densest of all the planets.
Scales Of The Universe » This Distance Is Equal To 9.46 X 1015 M Or 9500 Billion Km. Light Year Is The Unit Of Distance. 1 Parsec = 3.26 Light Years
The Size Of The Earth
- The Shape Of The Earth Is In The Form Of A Sphere Which Is Fixed At The Poles. It Appears To Inflate Slightly From The Poles Towards The Equator.
- This Viscosity Is Due To The Centripetal Force Of The Earth.
- The Actual Size Of The Earth Is ‘Geoid’, Which Means The Earth Is The Size Of The Earth .
Earth » Perihelion
Nearest Position From The Sun. Earth Comes To This Position On January 3 Each Year. This Distance Is About 147 Million Km From The Sun.
Earth » Aphelion
- Farthest Position From The Sun. Earth Comes To This Position On 4 June Every Year When It Is At A Distance Of 152 Million Km From The Sun.
- The Earth Rotates On Its Axis From West To East, That Is, Counter-Clockwise. It Takes 23 Hours, 56 Minutes And 4.09 Seconds To Complete One Rotation.
- Day And Night Occur On Earth Due To Daily Motion.
- Because Of Its Rotation On Its Axis, The Shape Of The Earth Is Not A Perfect Sphere.
- The Period Of Rotation On The Polar Axes Is Called A Constellation Day.
Earth » Revolutions ( Annual Speed )
- The Earth Revolves Around The Sun At A Speed Of 100,000 Km/H. It Takes 365 Days And 6 Hours To Complete One Revolution.
- This Additional Time Of 6 Hours Is Added To The Month Of February, Giving The Month Of February 29 Days Every Four Years. In This Way, Every Four Years There Is A Year Of 366 Days, Which Is Called A Leap Year.
- The Earth Attains Four Critical Positions While Orbiting The Sun.
- This Is Due To The Tilt Of The Earth On Its Axis.
- These Are Called Solstices And Equinoxes, On June 21, The Rays Of The Sun Fall Vertically On The Tropic Of Cancer. This Is Called The Summer Solstice.
- At This Time There Is Continuous Day At The North Pole And Continuous Night At The South Pole.
- On December 22, The Vertical Rays Of The Sun Fall On The Tropic Of Capricorn. This Is Called The Cold Solstice. Since The Earth’s Path Of Revolution Is Elliptical, The Distance Between The Earth And The Sun Varies.
- On 21st March And 23rd September The Position Of The Earth Is Such When The Sun’s Rays Are Read Vertically At The Equator. On This Date Day And Night Are Equal All Over The World. This Position Is Called The Equinoxes.
- The Vernal Equinox Occurs On 21 March And The Autumnal Equinox On 23 September.
| Theories/Concepts | Scientist/Philosopher |
|---|---|
| Gaseous Hypothesis | Immanuel Kant |
| Nebula Hypothesis | Laplace |
| Planetary Hypothesis | Chamberlin And Moulton |
| Tidal Hypothesis | Jeans & Jefferies |
| Dual Hypothesis | Russell |
| Supernova Hypothesis | Hoyle |
| Interstellar Dust Hypothesis | Autoshmid |
| Shephid Hypothesis | A C Banerjee |
| Jupiter-Sun Duality Hypothesis | Droboshevsky |
| The Big Bang Theory | Georges Lematre |
1. What is Earth?
Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system and the only known celestial body to support life. It is the fifth-largest planet by diameter and the densest of all the planets.
2. What is the Earth’s structure?
Earth consists of several layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the outermost layer and is divided into continental and oceanic crusts.
3. How many countries are there in the world?
There are 195 countries in the world today. This total comprises 193 countries that are member states of the United Nations and 2 countries that are non-member observer states: the Holy See and the State of Palestine.
4. What is the diameter of the Earth?
The diameter of the Earth is approximately 12,742 kilometers (7,918 miles).
5. What is the Earth’s atmosphere made of?
The Earth’s atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (about 78%), oxygen (about 21%), and trace amounts of other gases like carbon dioxide, argon, and water vapor.
6. What are the Earth’s major landforms?
Major landforms on Earth include mountains, hills, plateaus, plains, valleys, deserts, and various bodies of water like oceans, seas, lakes, and rivers.
7. How much of the Earth’s surface is covered by water?
Approximately 71% of the Earth’s surface is covered by water, mostly in the form of oceans and seas.
8. What is the Earth’s climate like?
The Earth’s climate varies across regions, influenced by factors like latitude, altitude, proximity to water, and prevailing wind patterns. It includes climates ranging from arid deserts to polar ice caps.
9. What is the Earth’s rotation and revolution period?
The Earth takes approximately 24 hours to complete one full rotation on its axis (a day), and about 365.25 days to orbit the Sun (a year).
10. What are the Earth’s natural resources?
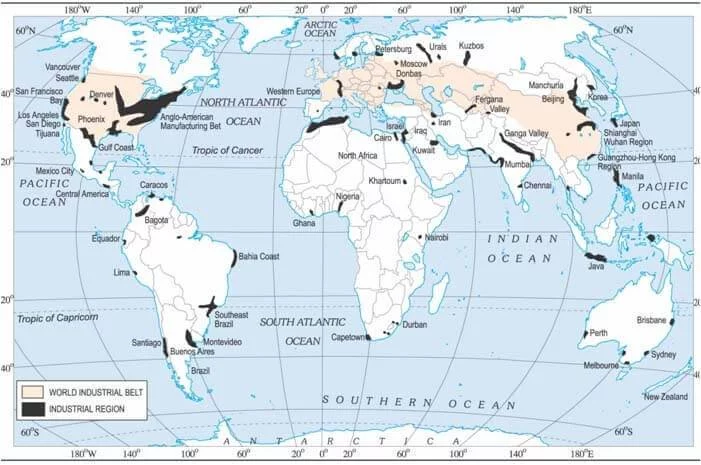
Earth’s natural resources include minerals, fossil fuels, fresh water, forests, wildlife, and fertile soil, all of which are essential for sustaining life and supporting various industries.
11. How is Earth’s biodiversity important?
Earth’s biodiversity, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance, supporting ecosystems, and providing resources essential for human survival.
12. How Many Country In Earth?
195 countries
5/5 - (1 vote)